

Subsequent failures can permit these radioisotopes to breach further layers of containment. Once the fuel elements of a reactor begin to melt, the fuel cladding has been breached, and the nuclear fuel (such as uranium, plutonium, or thorium) and fission products (such as caesium-137, krypton-85, or iodine-131) within the fuel elements can leach out into the coolant. Alternatively, an external fire may endanger the core, leading to a meltdown. A meltdown may be caused by a loss of coolant, loss of coolant pressure, or low coolant flow rate or be the result of a criticality excursion in which the reactor is operated at a power level that exceeds its design limits. This differs from a fuel element failure, which is not caused by high temperatures. It has been defined to mean the accidental melting of the core of a nuclear reactor, however, and is in common usage a reference to the core's either complete or partial collapse.Ī core meltdown accident occurs when the heat generated by a nuclear reactor exceeds the heat removed by the cooling systems to the point where at least one nuclear fuel element exceeds its melting point.
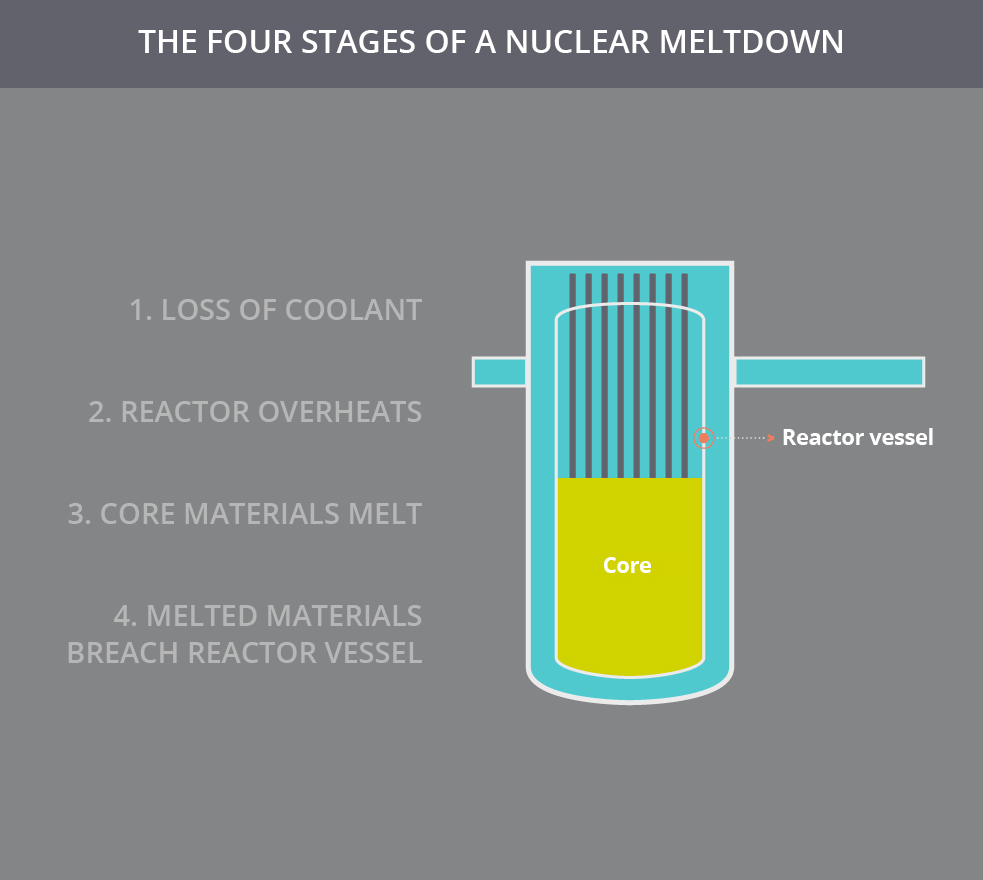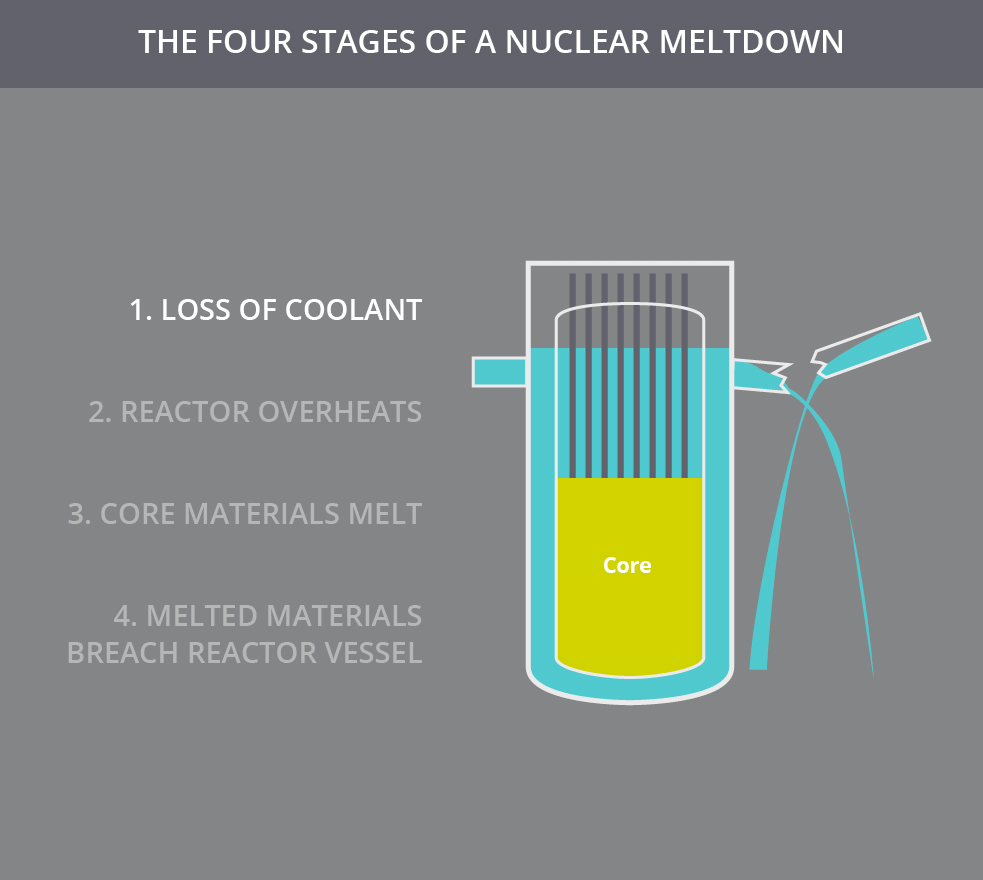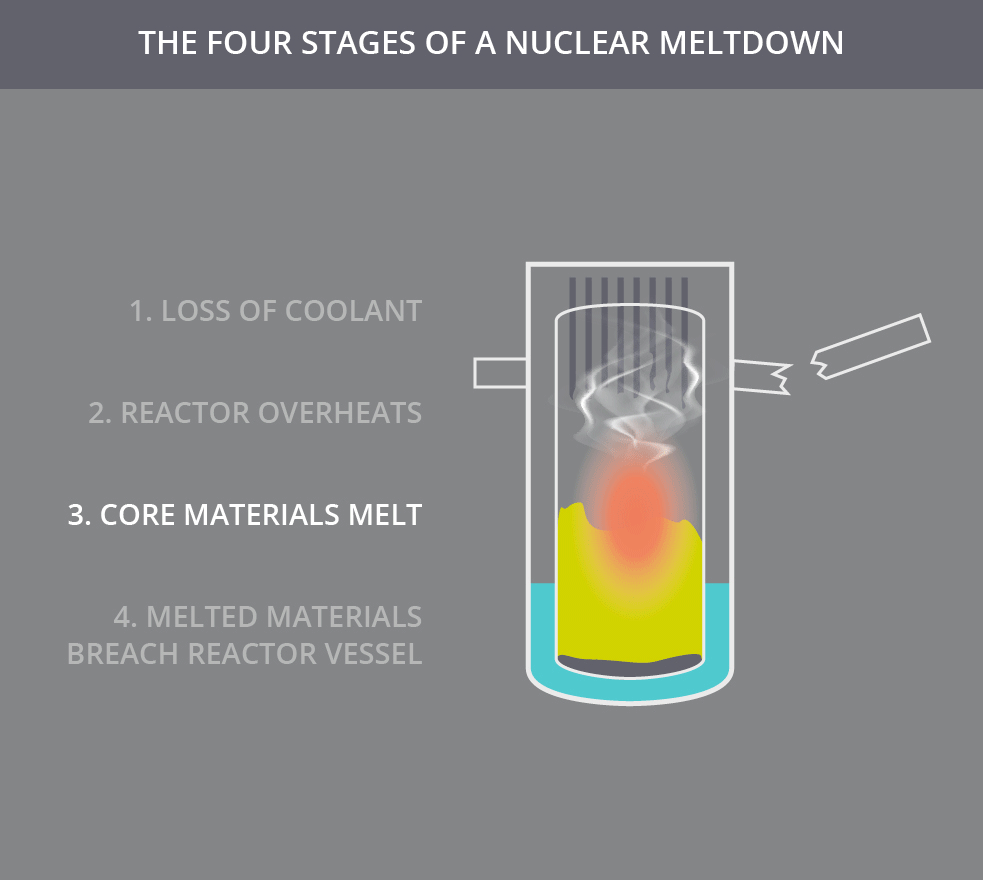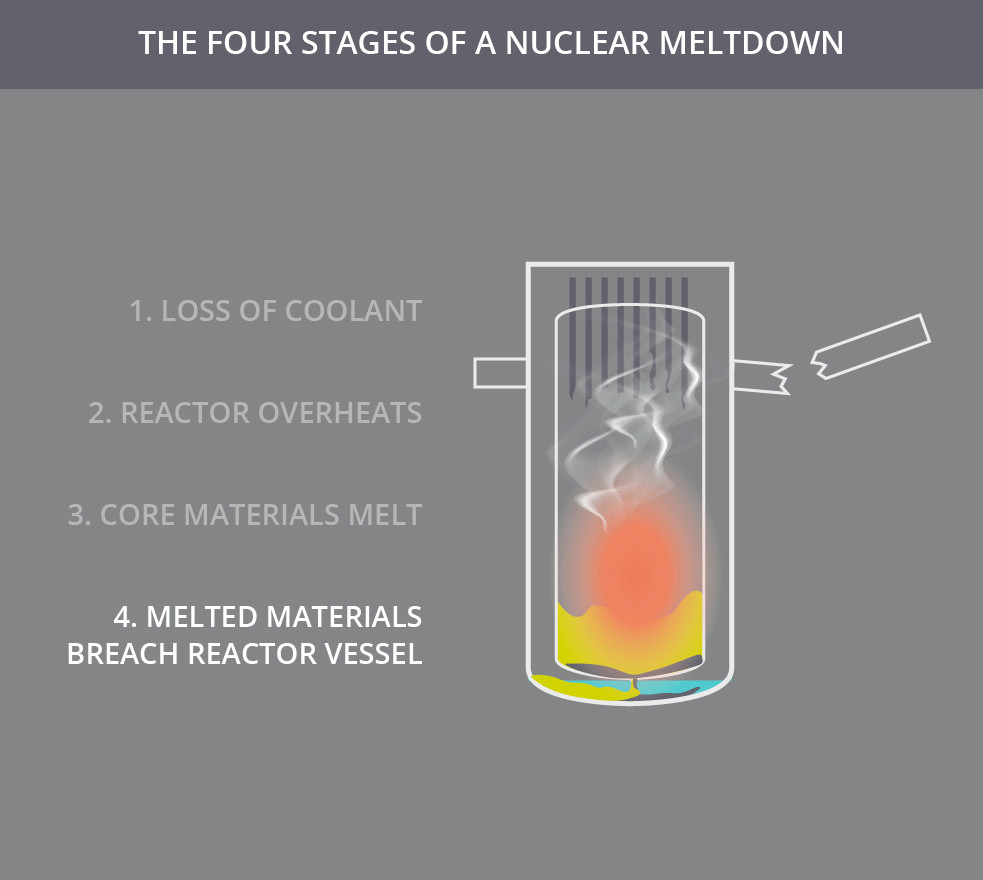
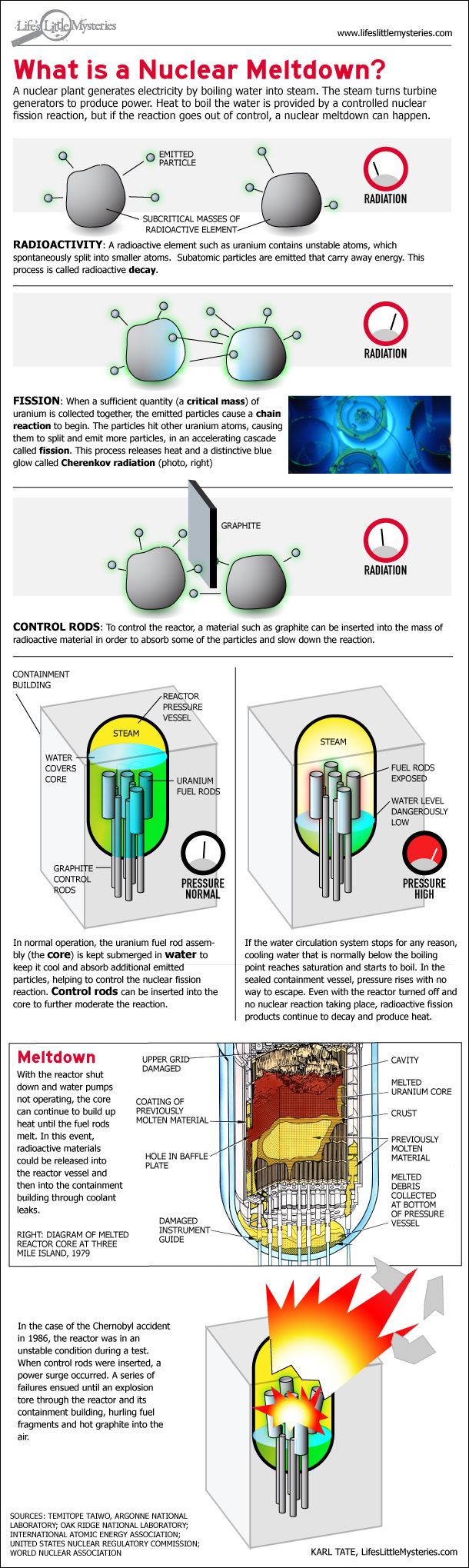
The term nuclear meltdown is not officially defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency or by the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Unit 2, which suffered a partial core melt, is in the background.Ī nuclear meltdown ( core meltdown, core melt accident, meltdown or partial core melt ) is a severe nuclear reactor accident that results in core damage from overheating. Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station consisted of two pressurized water reactors manufactured by Babcock & Wilcox, each inside its own containment building and connected cooling towers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
